Quote for : POSH At The Workplace E-Learning
We will be in touch shortly at
As an employer, your role transcends beyond business operations and profit margins; it extends to creating
and maintaining a workplace where safety, respect, and equality are ideals and everyday realities. The
Prevention of Sexual Harassment (POSH) Act in India reinforces this responsibility, mandating a secure and
dignified work environment for all employees. However, the essence of POSH training goes beyond legal
compliance; it's about nurturing a workplace culture where every individual feels valued, heard, and
protected.
You might recognize the critical need for POSH
training but wonder about its tangible impact.
Sexual harassment in the workplace is a complex challenge that, if unaddressed, can erode the core of your
organization's culture, affecting employee morale, productivity, and even your company's reputation.
Equipping yourself and your team with a deep understanding of what constitutes sexual harassment, the legal
obligations under the Indian POSH Act, and effective redressal mechanisms is prudent and imperative.
Acknowledging this essential need, PlayAblo has developed a comprehensive POSH training
course tailored for
today's dynamic workplace environments, accessible through our advanced Learning Management
System.
Our
objective is to empower you with actionable insights and practical tools to meet the legal requirements and
to lead by example in fostering a workplace that champions respect and dignity for all.
With PlayAblo's LMS, this POSH training course is designed to be engaging, interactive, and easily
integrated into your existing training programs, ensuring that the principles of POSH are seamlessly woven
into the fabric of your organization's culture.
Our POSH training materials are tailored to demystify the legal landscape - offering you a clear, actionable framework to navigate its requirements. But we go beyond mere compliance. Our POSH trainer certification curriculum delves into an in-depth analysis of what truly constitutes sexual harassment, challenging common misconceptions and illuminating the subtle dynamics that often go unnoticed.
The Indian POSH Act, officially titled the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
(Prevention,
Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013, is a landmark piece of legislation that seeks to protect women from
sexual harassment at their place of work.
This Act was a response to the 1997 Supreme Court judgment in the case of Vishaka and others v. State of
Rajasthan, which recognized sexual harassment as a violation of the fundamental rights of women to
equality under Articles 14 and 15 of the Indian Constitution, and their right to life and to live with
dignity under Article 21.
The Indian POSH Act was necessitated by the urgent need to provide a safe working environment for women,
where their fundamental rights are respected and protected. Before the enactment of this law, workplace
harassment was addressed under various sections of the Indian Penal Code and the Indian Evidence Act,
without a singular focus on sexual harassment or a standardized procedure for redressal.
The POSH Act's roots lie in the international commitment to gender equality and human rights, particularly
the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), to which India is
a signatory.
The Vishaka Guidelines, laid down by the Supreme Court in 1997, served as the de facto law for addressing
workplace sexual harassment in India until the POSH Act was enacted in 2013. These guidelines were
instrumental in shaping the provisions of the Indian POSH Act, ensuring a more robust and comprehensive
legal framework.
The Indian POSH Act includes several key components that collectively aim to create a safer work environment for women:
The Act provides a broad definition of sexual harassment to include any unwelcome act or behavior, whether directly or by implication, such as physical contact, a demand or request for sexual favors, making sexually colored remarks, showing pornography, or any other unwelcome physical, verbal, or non-verbal conduct of a sexual nature.
The Indian POSH Act mandates employers to take steps to prevent sexual harassment by creating a policy against sexual harassment, conducting employee awareness and training programs, and creating a conducive environment for reporting incidents without fear of reprisal.
Employers are required to constitute an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) at every office or branch with 10 or more employees. The Act lays down the process for the resolution, settlement, or prosecution of sexual harassment complaints, including the provision for an appeal.
The Indian Posh Act outlines a detailed process for the complaint and inquiry that needs to be followed by the ICC, including the timeline for submitting a complaint, the inquiry process, and the action to be taken upon the conclusion of the inquiry.
The Act also provides safeguards against malicious or false accusations of sexual harassment, including provisions for action to be taken against individuals making false allegations.
The Indian POSH Act represents a significant advancement in the Indian legal system's approach to dealing with sexual harassment in the workplace. By providing a clear definition of harassment, outlining the responsibilities of employers, and setting up a mechanism for the redressal of complaints, the Act aims to ensure that women can work in an environment free from harassment and discrimination, thus enabling them to work to their fullest potential.
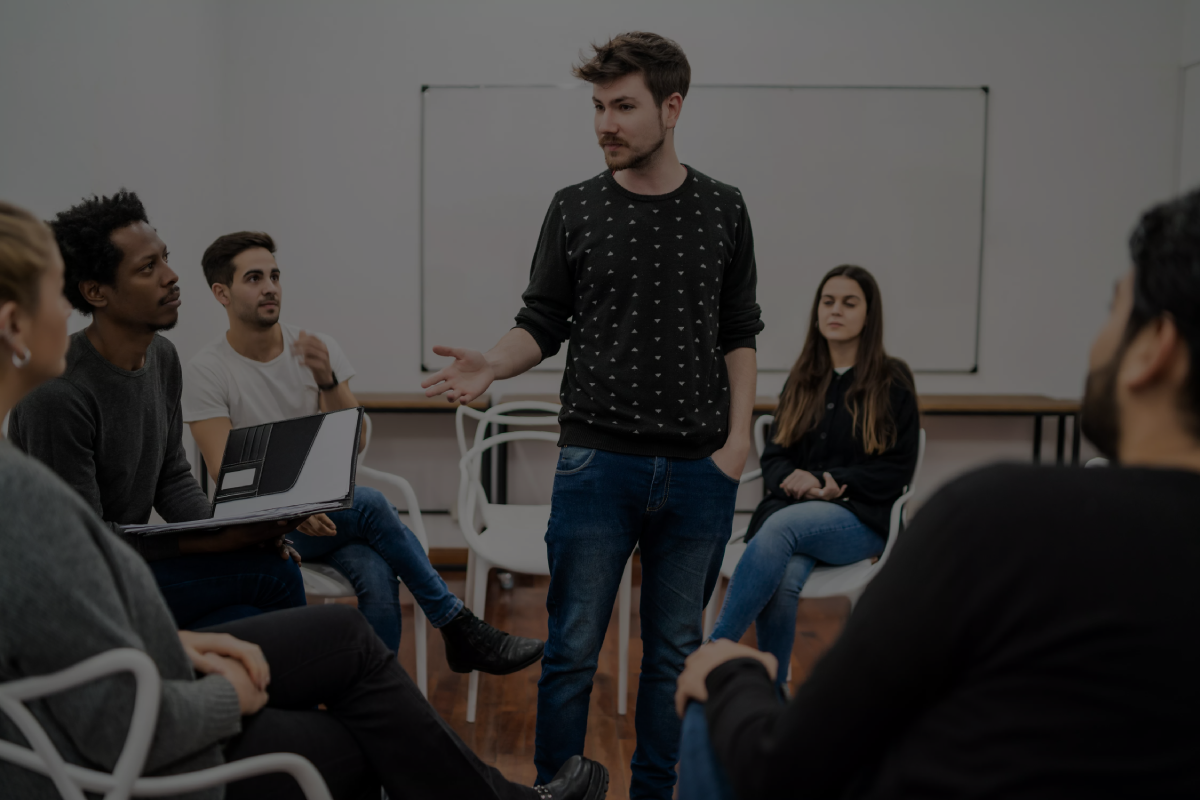
Understanding what constitutes sexual harassment under the Prevention of Sexual Harassment Act is crucial for maintaining a respectful and safe workplace. The Act defines sexual harassment broadly to include any unwelcome act or behavior with a sexual connotation. This expansive definition ensures that various forms of inappropriate behavior are covered, from overt physical contact to subtler forms of harassment that might not be immediately recognized as such.
Any unwelcome physical contact, including touching, patting, pinching, or brushing against an individual's body, falls under sexual harassment.
This includes any unwelcome verbal or non-verbal conduct where submission to such conduct is made a term or condition of an individual's employment or is used as a basis for employment decisions.
Comments, jokes, or gestures that are of a sexual nature and make the recipient uncomfortable constitute sexual harassment.
The display of pornographic or sexually explicit images, videos, or material in the workplace is a clear form of sexual harassment.
This catch-all category covers a wide range of actions, from leering and stalking to sending unwelcome sexually suggestive texts or emails.
● A manager making unwelcome advances towards a subordinate with implications that favoritism in
promotion
or assignment could follow compliance.
● Colleagues engaging in "banter" that includes explicit sexual jokes or innuendos directed at or in the
presence of someone who finds it offensive.
● Sharing sexually explicit content via email or social media platforms within the workplace, creating
an
uncomfortable environment.
● Unwanted, deliberate physical contact, such as "accidental" brushing up against someone or unnecessary
touching during conversations.
A key aspect often misunderstood is the role of consent. Any behavior that is not mutually welcome or reciprocated can be considered harassment, even if there was no intention to harass.
Harassment often involves a misuse of power, not necessarily limited to hierarchical relationships but also in instances where the harasser holds some form of influence over the victim's career or work environment.
What might be considered acceptable behavior in one cultural context could be viewed as inappropriate or harassing in another, making sensitivity to cultural differences vital.
It's important for both employers and employees to recognize these behaviors and understand the broad scope of what can constitute sexual harassment under the Indian POSH Act. This awareness is essential in fostering a workplace environment that is safe, respectful, and inclusive for everyone.
It's imperative to understand and implement the formal processes for lodging and resolving complaints of sexual harassment in the workplace, as outlined by the Prevention of Sexual Harassment Act. A cornerstone of this process is the effective management and operation of the Internal Complaints Committee, which you are mandated to establish.
Under the Indian POSH Act, you are required to constitute an Internal Complaints Committee at every office
or branch of your organization with 10 or more employees. The ICC must be composed of:
● A presiding officer (who must be a woman at a senior level in your organization)
● Not less than two members from among your employees who have a background in social work or legal
knowledge
● An external member from an NGO or association committed to the cause of women or familiar with issues of
sexual harassment
Upon receiving a written complaint of sexual harassment, the ICC is tasked with initiating and conducting a thorough and confidential inquiry. The process must be carried out with sensitivity, ensuring the dignity and privacy of all involved parties are maintained.
The ICC has the authority to recommend to you, as the employer, any interim relief measures for the complainant, such as transfer, leave, or any other appropriate action, to prevent further harassment or victimization during the inquiry.
Should the ICC find the allegations to be substantiated, they must recommend to you the necessary disciplinary actions against the perpetrator, which could range from a written apology to termination, depending on the severity of the case. Additionally, the ICC may suggest remedial measures for the complainant.
A critical function of the ICC is to ensure that the complainant and any witnesses are protected from retaliation or victimization for coming forward or participating in the inquiry process.
As an employer, your role is to ensure the formation and proper functioning of the ICC and to foster an organizational culture where such complaints are taken seriously, and the redressal process is accessible and trusted. By adhering to the guidelines set forth by the Indian POSH Act and empowering the ICC to perform its duties effectively, you contribute to creating a safer, more respectful workplace where every employee's rights and dignity are upheld.


As managing one’s ethical compass becomes challenging in the arena of business. it is important...

Most studies that list skills necessary in the workplace – be it for team success, conflict management...
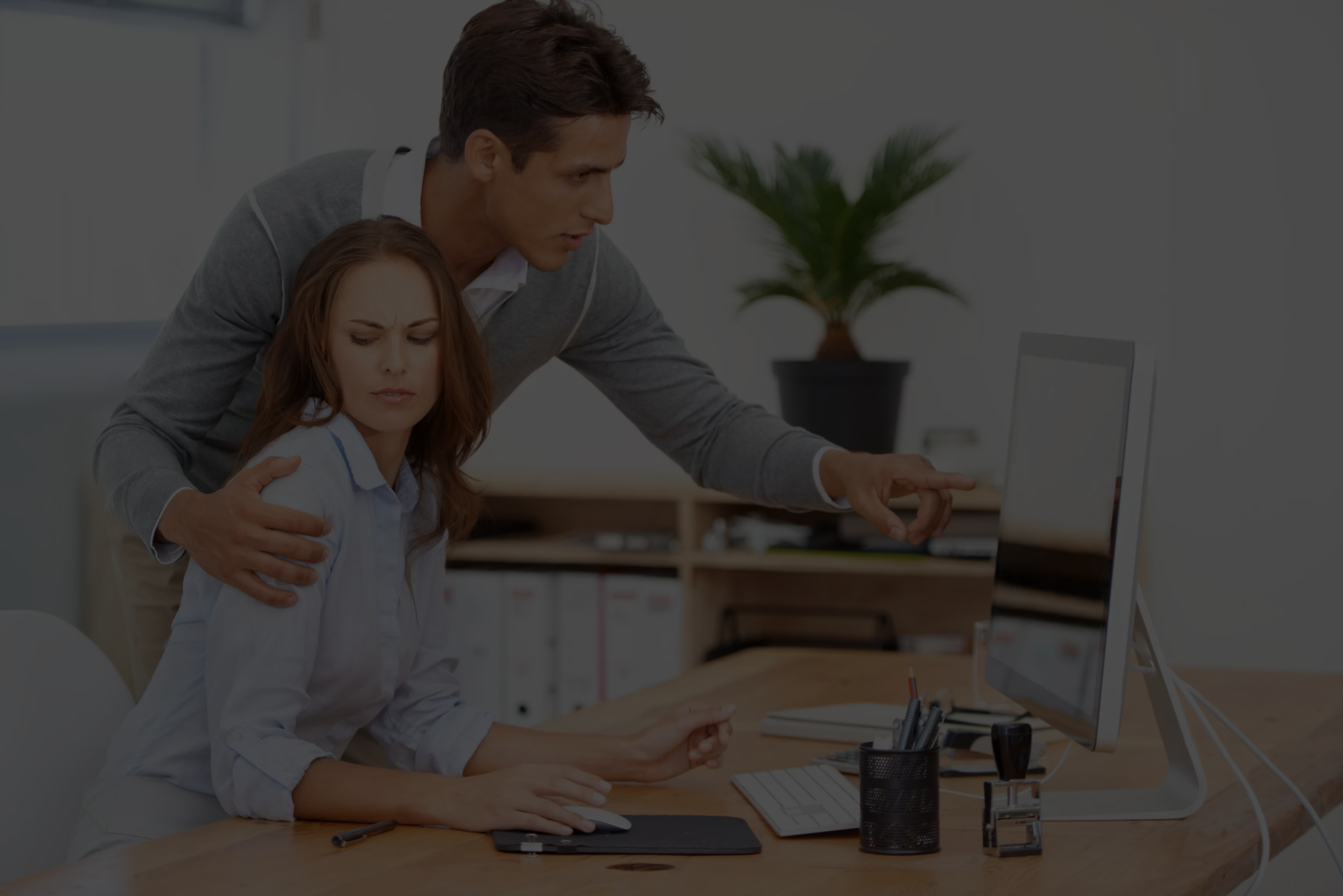

The constitution guarantees equality and protection of life and personal liberty. The psychological...

As organizations adapt to suitable remote working practices it is necessary for employees in any ...

Strong teams build successful organizations. Team success is determined by aspects that bond...

Plans are most effective when time is made to execute them. In both our personal spaces and our...

The greatest asset of any organization is its customers. The salespeople are the ones who build...

India’s pharmaceutical industry With its strong manufacturing base of pharmaceutical products and...

Gain a competitive edge in the modern workplace by developing proficiency in Microsoft Word...

Organizations that do businesses with EU residents and collect their personal data have to comply with Generation...

At the core of any thriving organization lies its customer base, and the individuals responsible for...