When we talk about skills transformation, we’re referring to the process of acquiring new skills or updating existing ones to adapt to the changing demands of the job market. Skills evolution is becoming increasingly important for workers of all levels and industries in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world.
As per research, in the near future, half of all employees will need to have developed new skills to keep up with the changes in the job market. However, according to a recent Global Skills Report, 48% of businesses list a skills and talent deficit as their most pressing matter in the coming three years.

The difference in how well-performing companies handle this skills deficit from underperformers may be less startling. Leading businesses in the world are leveraging skills to forge new paths and support the success of their employees in the changing workplace.
In other words, while underperformers are substantially more likely to postpone skills development initiatives, high-performing firms prioritize talent management as the best method to close skill shortages.
And it’s not just low-skilled jobs that are at risk of being replaced by automation – even jobs that were once thought to be safe, such as those in finance and healthcare, are now being impacted.
As you can see, the importance of skills transformation in the future workforce cannot be overstated. With so many jobs changing and new industries emerging, it’s crucial for workers to continuously update their skills in order to stay competitive in the job market.
By investing in skills transformation, individuals can increase their chances of finding and keeping a job and open up new career growth and advancement opportunities. Let’s dig down into this in more detail.
Table of Contents
The Current State of Skills in the Workforce

One of the biggest challenges facing the workforce today is the so-called “skills gap.” This refers to the disconnect between the skills that workers have and the skills that employers need.
According to the National Federation of Independent Business, 42% of owners have job openings that cannot be filled, a record high. 91% of those hiring or trying to hire report few or no qualified applicants for the positions they were trying to fill.
The skills gap affects both individual workers and employers and has a broader impact on the economy. When positions go unfilled, it can slow down productivity and impede economic growth. As per a report by We Forum, closing the skills gap could boost global GDP by $2.5 trillion by 2030.
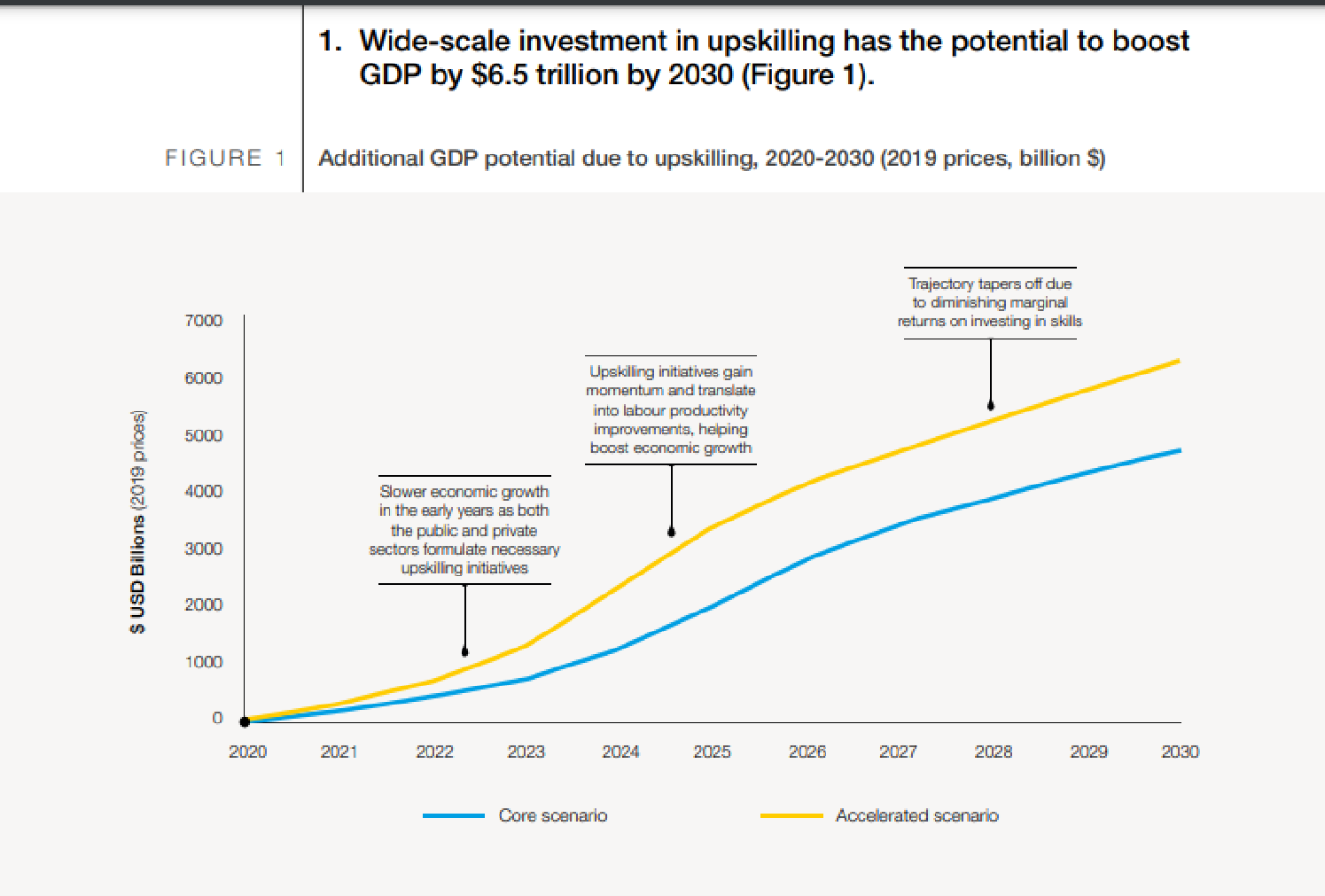
Technology is a major driver of the emerging skills transformation. As automation and other forms of technology continue to advance, they are changing how we work and the skills needed to do so.
For example, the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning has led to a growing demand for workers with skills in data analysis and programming.
At the same time, technology is also making certain skills and jobs obsolete, such as data entry and customer service positions that chatbots and other automated systems can now handle.
To understand the current state of skills in the workforce, it is important to acknowledge the significant role of technology in shaping the skills needed in the future. With technology advancing at a rapid rate, it is more important than ever for individuals to continuously learn and adapt to stay relevant in the job market.
Essential Skills in the Futuristic Workplace
The rise of automation and its impact on the workforce is one of the most significant changes that will shape the future of work. By 2030, as many as 800 million jobs could be displaced by automation, while 375 million workers may need to switch occupational categories and learn new skills.
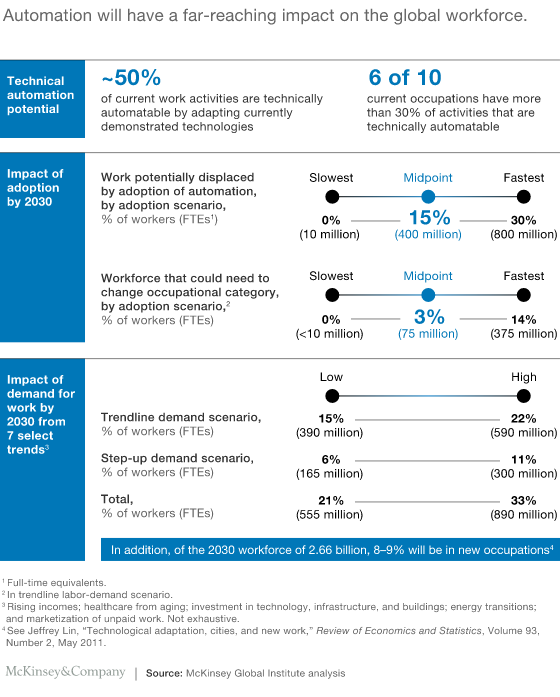
The jobs most at risk of being automated are those that involve repetitive tasks and data collection, such as those in manufacturing and transportation.
However, automation is not all bad news for workers. In fact, it can free workers from menial tasks and allow them to focus on more creative, higher-skilled work. For example, using automation in healthcare can allow doctors and nurses to spend more time with patients and less on paperwork.
The shift towards a knowledge-based economy is another trend that will shape the future of work. In a knowledge-based economy, the most valuable asset is not physical resources or labor but knowledge and information.
The rise of the internet and other digital technologies has made it easier for people to access and share information and has led to a growing demand for workers with skills in areas such as data analysis, digital marketing, and web development.
The emergence of new industries is another trend that will shape the future of work. With technology advancing at a rapid pace, new industries are emerging all the time, such as the gig economy, e-commerce, and renewable energy.

These new industries require different skills than those needed in traditional industries, and workers will need to be able to adapt to these changes in order to stay competitive in the job market.
For example, the gig economy, which refers to the growing number of people who work as freelancers or independent contractors, requires workers to have skills such as self-motivation and time management.
In summary, the future of work is going to be shaped by a number of factors, including automation, the shift towards a knowledge-based economy, and the emergence of new industries. Workers will need to continuously learn and adapt in order to stay competitive in the job market.
As the pace of technological change continues to accelerate, it is important to invest in skills transformation early to stay ahead of the curve and be ready for the opportunities that the future of work will bring.
Strategies for Skills Transformation to Make Your Workforce Future-ready

Fostering Upskilling and Reskilling
One of the most effective ways to address the skills gap and prepare workers for the future of work is through upskilling and reskilling programs.
These programs help workers acquire new skills and knowledge that are in demand in the job market. They can take many forms, including online courses, apprenticeships, and on-the-job training.
Upskilling refers to the process of acquiring new skills to move up in a current occupation, while reskilling refers to the process of learning new skills to transition to a completely new occupation.
These programs can be tailored to the specific needs of individual workers and employers and can be delivered through a variety of formats, such as online learning, classroom-based instruction, or on-the-job training.
Encouraging a Culture of Collaboration
Collaboration between employers, government, learning providers, and educational institutions is another key strategy for skills transformation. Employers can play a critical role in identifying the skills needed in the job market and providing training and development opportunities for their employees.
The government can help by investing in education and training programs and creating policies supporting lifelong learning. Learning providers like PlayAblo can help by developing curricula and training programs that align with the job market’s needs.
Offering Lifelong Learning

Emphasis on lifelong learning is another important strategy for skills transformation. As technology continues to advance and the job market evolves, workers will need to continuously learn and adapt in order to stay competitive.
This means that learning should be seen as a lifelong endeavor, not just something that happens during formal education. Lifelong learning can take many forms, including online courses, workshops, and on-the-job training.
In addition, the use of technology in learning is becoming increasingly prevalent and can help to make learning more accessible, effective, and efficient. Virtual and augmented reality, gamification, microlearning, mobile learning, and artificial intelligence are among the technologies being used to enhance learning and training for skills evolution in workplaces.
Putting Employees in Charge of Their Learning
77% of business executives agree their organization should help their workers become more employable with relevant skills, but only 5% strongly agree they are investing enough in helping people learn new skills to keep up with the changing world of work. [Source]
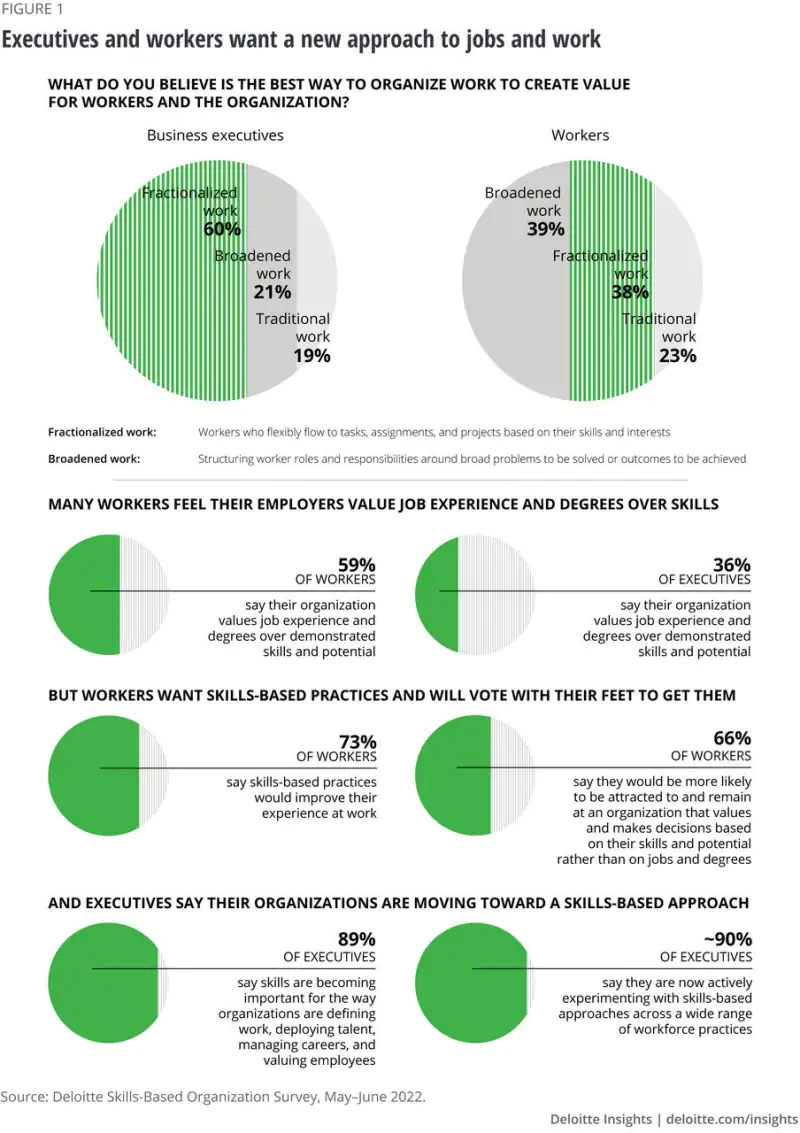
Professionals are still not sure that their organizations are giving new skill development the attention it deserves, whether for issues of availability, attention, enough funds, or other factors.
It follows that the concept of a community that allows you to facilitate efficient learning with suggestions that are fairly tailored and straight to the worker is an extremely effective method of growing employees and involving them and giving them the impression that they count.
This is because today’s consumers demand engagement from businesses. They also desire control over the direction of their development. So, among the key strategies of new skills evolution in your workplace is to put the worker at the core and give them the knowledge they need to direct their own future organically.
Offering Continuous Support and Guidance
Another important strategy for skills transformation is to provide support for the most vulnerable workers, such as those with low skills or from disadvantaged backgrounds, to help them access training and employment opportunities. This can include targeted training programs, mentoring, and career counseling services.
Ad: PlayAblo’s Enterprise-Grade Micro-Learning platform is built for millennial learners. Micro-Learning, assessments, and gamification features ensure learning outcome measurement and sustained engagement.
Find out more and request a custom demo!
Building a Skills Tree
According to research, talents typically have a half-life” of around five years — with highly technical skills having a half-life of only around 21/2 years. Technical abilities have a limited lifespan. Thus continuing education is necessary to keep current.
The Chief Learning Officer Magazine claims that business executives and learners require a totally new framework for considering abilities, one that encourages consideration of novel issues:
- Durable vs. perishable skills
- Transferrable vs. non-transferrable skills
- Skills that are in demand now vs. long term
The CLO Magazine splits skill longevity into three groups to show how long-lasting a skill is:
- Perishable abilities: Less than 2.5 years of half-life. Perishable talents are often revised, organization-specific technical skills, company policy]ies and resources, and specialized procedures.
- Semi-durable abilities: 2.5 to 7.5 years of half-life. These are typically the conceptual frameworks and knowledge bases that give rise to industry-specific technologies, procedures, and tools.
- Durable abilities: More than 7.5 years for half-life. They serve as fundamental attitudes and behaviors. These include more core abilities including creative thinking, project planning, communication skills, and leadership.
It’s crucial to take into account how transferrable a certain set of abilities actually are as businesses and individuals prepare for a reboot and start thinking through a competencies renewal. Together with the talents’ longevity, this establishes a structure that may change to meet the organization’s evolving requirements.
Perishable skills transformation offers a quick return on investment, but it offers little adaptability within professional positions and working families.
The ability to offer fluid, longer-term contributions to the organization as they move through numerous professions over the period of their career is empowered by training that prioritizes durable skills. Using a tree-shaped paradigm to think about skills development could be more productive.
This tree’s roots are made of lasting skills, its branches are made of semi-durable structures, and its leaves, which are more perishable abilities, change with the years.
The goal is to develop a tree, which is towering and broad, grows throughout every season, feeds the roots that support the trunk, develops new branching skills, and nurtures the foliage that shifts as the seasons pass.
You are able to see attitude and contextual learning as crucial to the task in question thanks to this tree-shaped model. This dynamic model pushes employees to create abilities with a focus on their durability, replicability, and significance for positions that your business may have to fulfill in the future.
It’s a different way to think about skills transformation. Additionally, because the skills blend contains recent and pertinent in-demand abilities, it guarantees that as people their employability quotient keeps rising.
Wrapping It Up
In conclusion, the future of work is rapidly changing, and the skills required for success are continuously evolving. The world of work is rapidly shifting towards a knowledge-based economy, with a growing demand for skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity.
The rise of automation and the emergence of new industries are also shaping the skills transformation — needed for the future. The need for continuous learning and adaptability has never been more pressing. To meet these challenges, it is essential that we focus on skills transformation.
By working together, employers, government, learning providers, and educational institutions can help close the skills gap and prepare workers for the future workforce. Investing in upskilling and reskilling programs, promoting collaboration, and emphasizing lifelong learning will be key in ensuring that workers have the skills they need to succeed in the new economy.
It’s time to think beyond traditional learning methods and embrace new skills evolution to be ready for the future.
Ad: PlayAblo’s Enterprise-Grade Micro-Learning platform is built for millennial learners. Micro-Learning, assessments, and gamification features ensure learning outcome measurement and sustained engagement.
Find out more and request a custom demo!







Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.