What is competency mapping and why is it essential?
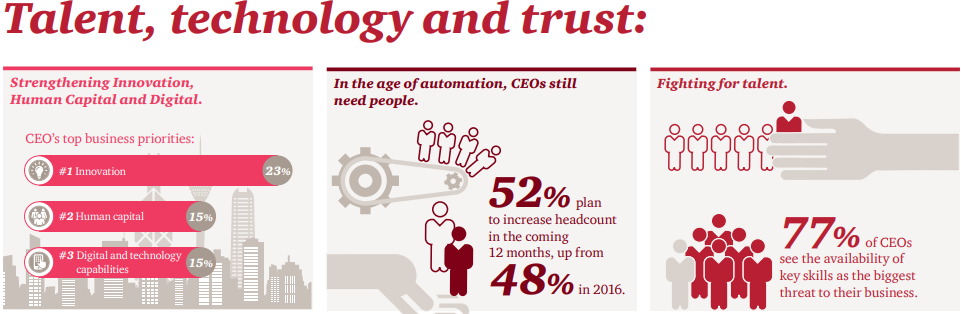
With 37% of CEOs expressing concern about the availability of key skills in their organizations, ensuring your team has the right competencies has become a top priority. In fact, a recent PwC report highlighted that 79% of CEOs see the lack of essential skills as a significant threat to their business. This highlights the urgency of addressing this gap. And to mitigate this problem, competency mapping emerges as an effective strategy to stay ahead.
Competency mapping is a strategic approach that helps you systematically identify and align the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviors needed for success in your organization. With the right implementation of this HR tool, you can witness significant improvements in talent management and workforce development.
By mapping out your employees’ competencies, you can clearly see where your team excels and where there’s room for growth, enabling you to create targeted development plans that drive both individual and organizational success. It provides a clear, actionable roadmap for your workforce’s growth and career advancement, making it easier to align their goals with the needs of the business.
But,
- How do you implement competency mapping effectively?
- How can you ensure it leads to tangible improvements in both individual and organizational performance?
That’s what this article is here to explore. We’ll guide you through the essential steps to integrate competency mapping into your talent development strategy, helping you keep up with the competition and lead the way in today’s competitive landscape.
Table of Contents
How Does Competency Mapping Help Talent Development?

When you know the specific competencies required for each role, it becomes much easier to see where your team stands and where they might need a little help. This knowledge allows you to create personalized development plans that address those gaps directly.
For your employees, competency mapping offers clear guidance on how they can grow. It gives them a roadmap, showing exactly what’s expected in their role and how they can advance within the company. This clarity is crucial for driving career growth and helping your team members develop in ways that are meaningful to both them and the organization.
From your perspective, competency mapping leads to better performance and alignment with your business goals. When your team has the right competencies, they’re better equipped to achieve what you need them to. This boosts performance and ensures your workforce is agile and ready to adapt to whatever comes next.
Competency Mapping vs. Traditional Skill Assessment
Competency mapping offers a more comprehensive approach than traditional skill assessments. While traditional assessments might focus on whether an employee can perform a specific task, competency mapping digs deeper. It looks at the full range of abilities, behaviors, and attitudes that contribute to success in a role.
For example, instead of just checking if someone can use a particular software, competency mapping examines how they use that software to solve problems, collaborate with colleagues, and contribute to the organization’s broader goals.
Here are the differences in detail:
| Aspect | Competency Mapping | Traditional Skill Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Holistic view of skills, behaviors, knowledge, and attitudes | Primarily focused on technical skills or specific tasks |
| Assessment Scope | Evaluates a combination of competencies, including soft skills | Typically assesses technical abilities or task-specific skills |
| Application | Considers how skills are applied in real-world scenarios | Focuses on whether a skill can be performed at a basic level |
| Development Approach | Supports long-term development and career growth | Often used for immediate performance evaluations |
| Outcome | Helps in identifying overall potential and readiness for future roles | Measures current ability to perform specific tasks |
| Example | Evaluates how well an employee collaborates, solves problems, and aligns with organizational goals | Tests proficiency in a specific software or process |
| Strategic Impact | Aligns employee competencies with organizational goals for future success | Addresses immediate skill gaps without broader strategic alignment |
| Employee Engagement | Provides a roadmap for career growth and skill development | May not clearly link to long-term career progression |
Now that you have an idea about competency mapping, let’s explore the steps to implement it in your organization:
Ad: PlayAblo’s Enterprise-Grade Micro-Learning platform is built for millennial learners. Micro-Learning, assessments, and gamification features ensure learning outcome measurement and sustained engagement.
Find out more and request a custom demo!
8 Steps to Implement Competency Mapping in Your Workplace
Implementing competency mapping in your organization is a systematic process that requires careful planning and execution. Below are the detailed steps you need to follow to effectively map competencies across your organization, ensuring that your workforce is aligned with your strategic goals.
Step 1: Define Organizational Competencies
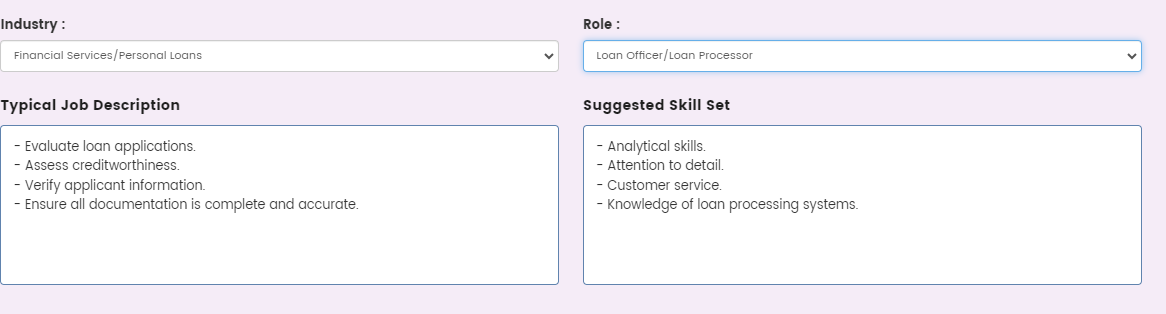
The first step in competency mapping is to identify and categorize the core competencies required across your organization. This process involves understanding the key skills, knowledge, behaviors, and attitudes that are essential for success at various levels of your organization.
- Identify Core Competencies:
- Organizational Competencies: These are the broad competencies that apply to everyone in the organization, regardless of role. They often reflect the company’s values, culture, and strategic priorities. For example, competencies like “innovation,” “customer focus,” or “adaptability” may be relevant across the board.
- Functional Competencies: These are specific to a particular department or function. For instance, financial analysis might be a core competency for the finance department, while project management could be critical for operations.
- Role-Specific Competencies: These are tailored to individual job roles. For example, a marketing manager might need competencies in “digital marketing,” “strategic thinking,” and “team leadership.”
- Categorize Competencies:
- Behavioral Competencies: These refer to the personal characteristics and behaviors that employees exhibit in the workplace. Examples include “communication skills,” “teamwork,” and “leadership.”
- Technical Competencies: These involve the specific technical skills and knowledge required for a role. Examples include “data analysis,” “software proficiency,” and “technical writing.”
By clearly defining and categorizing these competencies, you create a framework that can be used to assess current capabilities and identify areas for improvement.
Step 2: Involve Key Stakeholders
Engaging key stakeholders is crucial for the success of your competency mapping process. This step ensures that the competencies identified are relevant and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Engaging Leadership:
- Involve senior leaders early to gain their support and ensure the initiative aligns with the company’s strategic objectives.
- Leadership input is vital for identifying long-term competencies that reflect future business needs.
- Involving HR and Department Heads:
- HR facilitates the process, helping to integrate competencies into various HR functions such as recruitment, training, and performance management.
- Department heads provide valuable insights into the specific competencies required for success in their areas.
- Gathering Input:
- Use workshops, focus groups, or interviews to gather input from stakeholders across the organization. This collaborative approach ensures that the competencies are practical and relevant.
Step 3: Identify Competency Frameworks
Choosing the right competency framework is essential as it forms the foundation for your mapping process. A competency framework is a structured collection of competencies that are required to perform successfully in a given role or organization.
Overview of Popular Competency Frameworks
- SHRM Competency Model:
- Focuses on leadership, ethical practice, and business acumen, particularly suited for HR professionals.
- Lominger Competency Framework:
- Includes 67 competencies, covering personal, interpersonal, business, and leadership skills.
PlayAblo’s Competency Mapping Framework
Our framework guides you through identifying key roles, defining role expectations, listing required skills, conducting Training Needs Assessments (TNA), identifying skill gaps, and implementing targeted training to close these gaps.
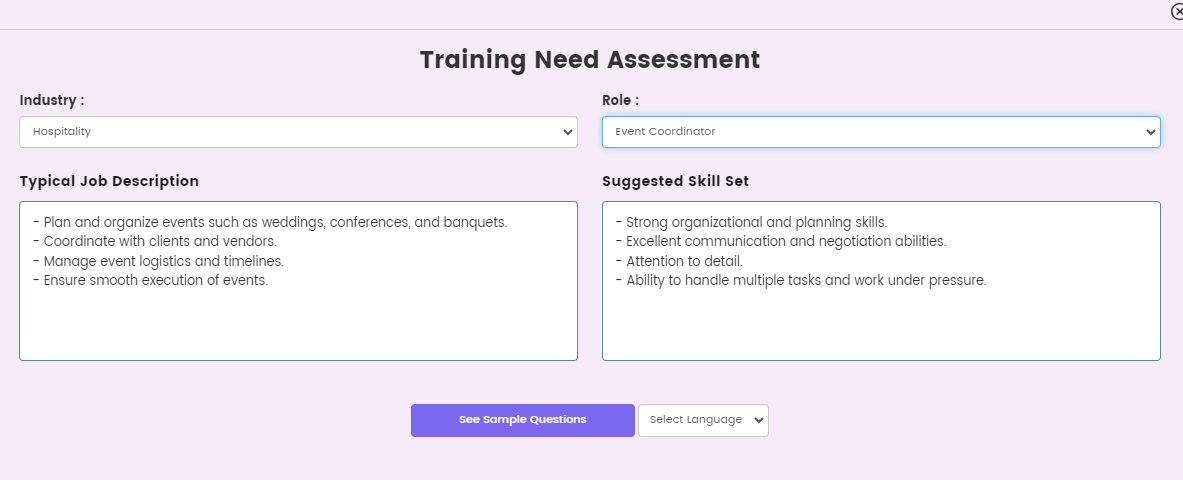
Here are the steps:
| Competency Mapping Framework | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Key Roles | Focus on essential roles within the organization that directly contribute to achieving business goals. |
| 2. Articulate Role Expectations | Define clear job descriptions, aligning them with organizational objectives. |
| 3. List Required Skills | Identify both hard and soft skills necessary for each role to succeed. |
| 4. Conduct TNA | Perform a Training Needs Assessment to compare current competencies with ideal skill sets. |
| 5. Identify Skill Gaps | Determine skill gaps at both the team and individual levels based on TNA results. |
| 6. Take Remediation Steps | Implement targeted training programs and resources to close the identified skill gaps and enhance overall competency. |
PRO TIP
When selecting a framework, consider whether to adopt an existing one, customize it, or develop a new one to fit your organization’s needs. Ensure that the chosen framework aligns with your business goals and reflects the competencies needed to achieve success.
Step 4: Develop Competency Profiles for Each Role

Once you have your competency framework, the next step is to create detailed competency profiles for each role within your organization. A competency profile outlines the specific competencies required for success in a given role, along with the expected proficiency levels.
Example Competency Profile for a Marketing Manager
- Strategic Thinking: Advanced proficiency required; involves developing and executing long-term strategies aligned with business goals.
- Digital Marketing Expertise: Expert proficiency needed; deep understanding of digital marketing channels and best practices.
- Team Leadership: Intermediate proficiency expected; ability to lead, motivate, and develop a team to achieve marketing objectives.
Each role’s competency profile should be tailored to its unique demands, ensuring the necessary competencies are clearly defined and actionable.
Step 5: Conduct Competency Assessments
Competency assessments are essential to understanding where your employees currently stand in relation to the required competencies. This step helps identify strengths and areas for development.
Methods for Assessing Competencies
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Assessment | Employees rate their own skills and behaviors against the competency profile. |
| 360-Degree Feedback | Feedback from peers, subordinates, and supervisors provides a comprehensive view. |
| Manager Evaluations | Managers assess employees based on direct observations and performance. |
Step 6: Analyze the Results
After conducting assessments, the next step is to analyze the data to identify skill gaps and development needs.
- Interpreting Assessment Data:
- Compare assessed competencies with the required proficiency levels to spot gaps.
- Identify common gaps across roles or departments to prioritize training initiatives.
- Using Data Analytics:
- Utilize data analytics tools to detect trends and patterns in competency levels.
- Analytics can also help in making informed decisions about talent development and succession planning.
Example: Competency Gap Analysis
| Competency | Required Proficiency | Current Proficiency | Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Thinking | Advanced | Intermediate | 1 Level |
| Digital Marketing Expertise | Expert | Advanced | 1 Level |
| Team Leadership | Intermediate | Basic | 2 Levels |
Step 7: Create and Implement Development Plans
Based on the identified gaps, create personalized development plans for each employee to help them reach the required competency levels.
- Designing Development Plans:
- Tailor the plans to address specific gaps. For example, if an employee needs to improve in “Team Leadership,” you might include mentorship opportunities or leadership training courses in their development plan.
- Integrating with Learning and Development Initiatives:
- Align these development plans with your organization’s broader L&D initiatives. This ensures that the training provided is relevant and supports both individual growth and organizational goals.
Example: Development Plan Activity
- Competency: Strategic Thinking
- Development Activity: Participate in a strategic planning workshop.
- Timeline: 3 months
- Competency: Team Leadership
- Development Activity: Enroll in a leadership development program.
- Timeline: 6 months
Step 8: Monitor Progress and Adjust
Ongoing monitoring is crucial to ensure that competency development is on track and to make necessary adjustments.
- Monitoring Progress:
- Regularly review the development plans to assess progress against goals.
- Use performance metrics and feedback to measure improvement in competencies.
- Adjusting Plans:
- Be flexible in modifying development plans based on feedback and changes in organizational needs.
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment help in achieving sustained competency development and overall employee performance enhancement.
Monitoring and Adjustment Strategies
| Monitoring Activity | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Regular Check-ins | Assess progress and make real-time adjustments to the plan. |
| Performance Reviews | Evaluate the impact of development activities on job performance. |
| Feedback Loops | Incorporate feedback from peers and managers to refine development plans. |
Best Practices for Effective Competency Mapping

Implementing competency mapping effectively requires thoughtful planning, clear communication, and a willingness to adapt as you go. Here are some best practices to ensure that your competency mapping initiative is successful and sustainable.
1. Start Small and Scale Gradually
Launching competency mapping across an entire organization can be overwhelming. Instead, start with a pilot program in a specific department or for a particular set of roles. This approach allows you to test your process, make adjustments, and demonstrate value before scaling up.
Tips for Piloting Competency Mapping:
- Select a Department or Role with High Impact: Choose a department where competency gaps are clearly visible, or where success in competency mapping can quickly demonstrate value. For example, piloting in the sales department could highlight immediate improvements in sales performance.
- Engage Enthusiastic Stakeholders: Involve team members who are open to change and willing to provide constructive feedback. Their buy-in can help smooth the process and encourage broader adoption when scaling.
- Document and Analyze Results: Keep detailed records of the pilot phase, including successes, challenges, and feedback. Use this data to refine your approach before rolling out competency mapping more broadly.
By starting small, you give yourself the opportunity to refine the process, troubleshoot potential issues, and build a strong foundation for a larger implementation.
2. Ensure Clear Communication
Clear communication is essential to the success of competency mapping. Employees need to understand not only what competency mapping is, but also why it’s being implemented and how it will benefit them and the organization.
Importance of Communication:
- Explain the Purpose: Clearly articulate the goals of competency mapping. Let employees know that the initiative is designed to help them grow in their careers, identify opportunities for development, and align their skills with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Highlight the Benefits: Emphasize how competency mapping will provide employees with clearer career paths, targeted development opportunities, and more meaningful feedback on their performance.
- Provide Regular Updates: Keep the lines of communication open throughout the process. Provide updates on the progress of the competency mapping initiative, share success stories, and address any concerns or questions that arise.
Effective communication helps to build trust and ensures that employees are engaged and supportive of the competency mapping process.
3. Leverage Technology
Technology can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of competency mapping. From assessment tools to data analytics platforms, there are numerous software solutions available that can facilitate the process.
Overview of Software and Tools:
- Competency Management Software: They offer comprehensive solutions for managing competencies. These tools allow you to create, assess, and track competencies across your organization.
- Assessment Tools: Such tools can be used to create customized assessments that align with your competency profiles. These tools make it easy to gather and analyze data from employees and managers.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Analytics tools can help you interpret assessment data, identify trends, and make informed decisions about talent development.
Ad: PlayAblo’s Enterprise-Grade Micro-Learning platform is built for millennial learners. Micro-Learning, assessments, and gamification features ensure learning outcome measurement and sustained engagement.
Find out more and request a custom demo!
Leveraging technology not only streamlines the competency mapping process but also provides valuable insights that can guide your talent management strategy.
4. Focus on Continuous Feedback and Iteration
Competency mapping is not a one-time project—it’s an ongoing process that should evolve with your organization’s needs. To keep it effective, it’s crucial to continuously gather feedback and be willing to make iterative updates to your competency framework.
Encouraging Feedback:
- Employee Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from employees on how the competency mapping process is working for them. Are the assessments fair? Do the development plans feel relevant? What improvements would they suggest?
- Stakeholder Input: Involve managers and department heads in reviewing the effectiveness of the competency mapping process. Their insights can help identify gaps or areas where the process could be improved.
Importance of Iterative Updates:
- Adapt to Organizational Changes: As your organization grows and changes, so too should your competency framework. Regularly review and update competencies to ensure they remain aligned with the strategic direction of the business.
- Refine Processes: Use the feedback and data collected to refine your competency mapping process. Whether it’s tweaking the assessment methods or adjusting the development plans, continuous improvement is key to maintaining the relevance and effectiveness of your competency mapping initiative.
Continuous Improvement Cycle for Competency Mapping
| Phase | Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback Collection | Gather insights from employees and managers | Identify strengths and areas for improvement |
| Data Analysis | Review data to detect trends and gaps | Make informed decisions on necessary changes |
| Framework Update | Adjust competencies based on feedback and data | Ensure continued alignment with organizational goals |
| Implementation | Roll out updated processes and frameworks | Maintain effectiveness and relevance |
By embracing continuous feedback and making iterative updates, you ensure that your competency mapping remains a dynamic tool that evolves with your organization, continually driving both employee and organizational growth.
Conclusion
Competency mapping is a powerful tool that, when implemented thoughtfully, can transform how your organization develops and utilizes talent. By starting small, communicating clearly, leveraging technology, and embracing continuous improvement, you can build a competency mapping framework that not only identifies and fills skill gaps but also drives long-term growth for both your employees and your organization. With these best practices in place, you’ll be well-equipped to align your workforce’s capabilities with your strategic goals, ensuring success in an ever-changing business landscape.
Ad: PlayAblo’s Enterprise-Grade Micro-Learning platform is built for millennial learners. Micro-Learning, assessments, and gamification features ensure learning outcome measurement and sustained engagement.
Find out more and request a custom demo!





